Educational Insights on Balanced Diet for Men
Explore the fundamentals of nutrition, understand the role of essential nutrients, and learn about maintaining a balanced approach to daily eating habits.

Introduction to Balanced Diet
A balanced diet refers to the practice of consuming a variety of foods in appropriate proportions to meet the body's nutritional needs. This includes adequate intake of macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as essential micronutrients like vitamins and minerals.
Understanding the principles of balanced nutrition helps individuals make informed decisions about their daily food choices. The concept emphasizes variety, moderation, and the importance of including different food groups in regular meals.
Importance of Macronutrients
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source for the body. They are found in foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and are an important part of a balanced diet.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for tissue repair, muscle maintenance, and various metabolic processes. They can be obtained from both animal sources like fish, poultry, and dairy, as well as plant sources such as beans, lentils, and nuts.
Fats
Dietary fats play a crucial role in hormone production, nutrient absorption, and cell membrane structure. Healthy fat sources include nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish.
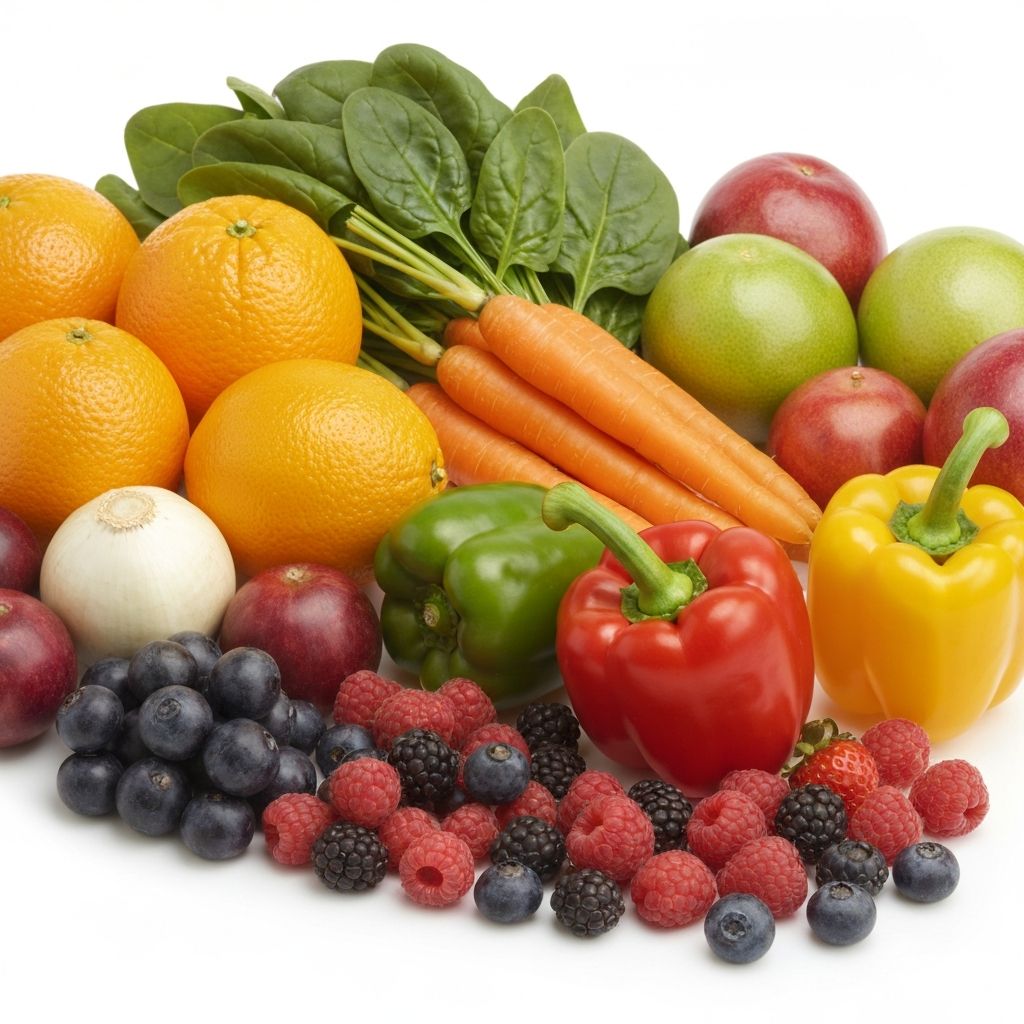

Vitamins and Minerals Overview
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients that support numerous bodily functions, from immune system health to bone strength and energy metabolism. Each vitamin and mineral has specific roles in maintaining overall health.
These nutrients are found in various foods, with fruits and vegetables being particularly rich sources. A diverse diet that includes different colored produce can help ensure adequate intake of these essential compounds.
Hydration and Energy
Proper hydration is fundamental to maintaining bodily functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal. Water is the most essential nutrient, and adequate fluid intake supports overall health and daily energy levels.
The relationship between nutrition and energy is complex. The body derives energy from the foods we consume, particularly from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Understanding this connection can help individuals make choices that support their daily activities and lifestyle.
Meal Planning Tips
Meal planning involves organizing meals in advance to ensure nutritional balance throughout the day. This practice can help individuals incorporate a variety of food groups and maintain consistent eating patterns.
Variety
Including different types of foods from all food groups helps ensure a wide range of nutrients. This approach encourages trying new ingredients and recipes.
Portion Awareness
Understanding typical portion sizes can help individuals gauge appropriate amounts of different foods. This knowledge supports balanced eating habits.
Meal Timing
Regular meal patterns can help maintain stable energy levels throughout the day. The timing and frequency of meals vary based on individual schedules and preferences.
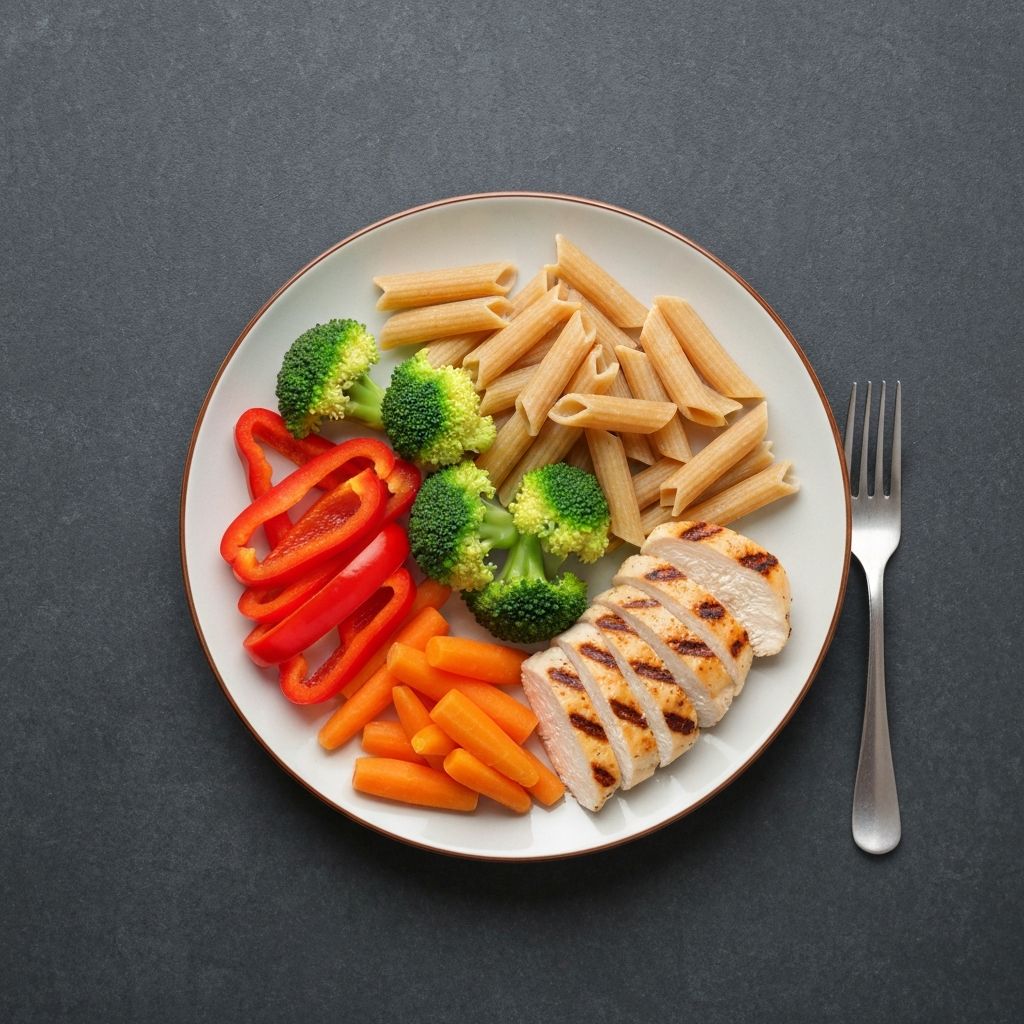
Key Food Groups
Understanding different food groups and their nutritional contributions is fundamental to balanced eating. Below are three important categories of foods that play distinct roles in a varied diet.
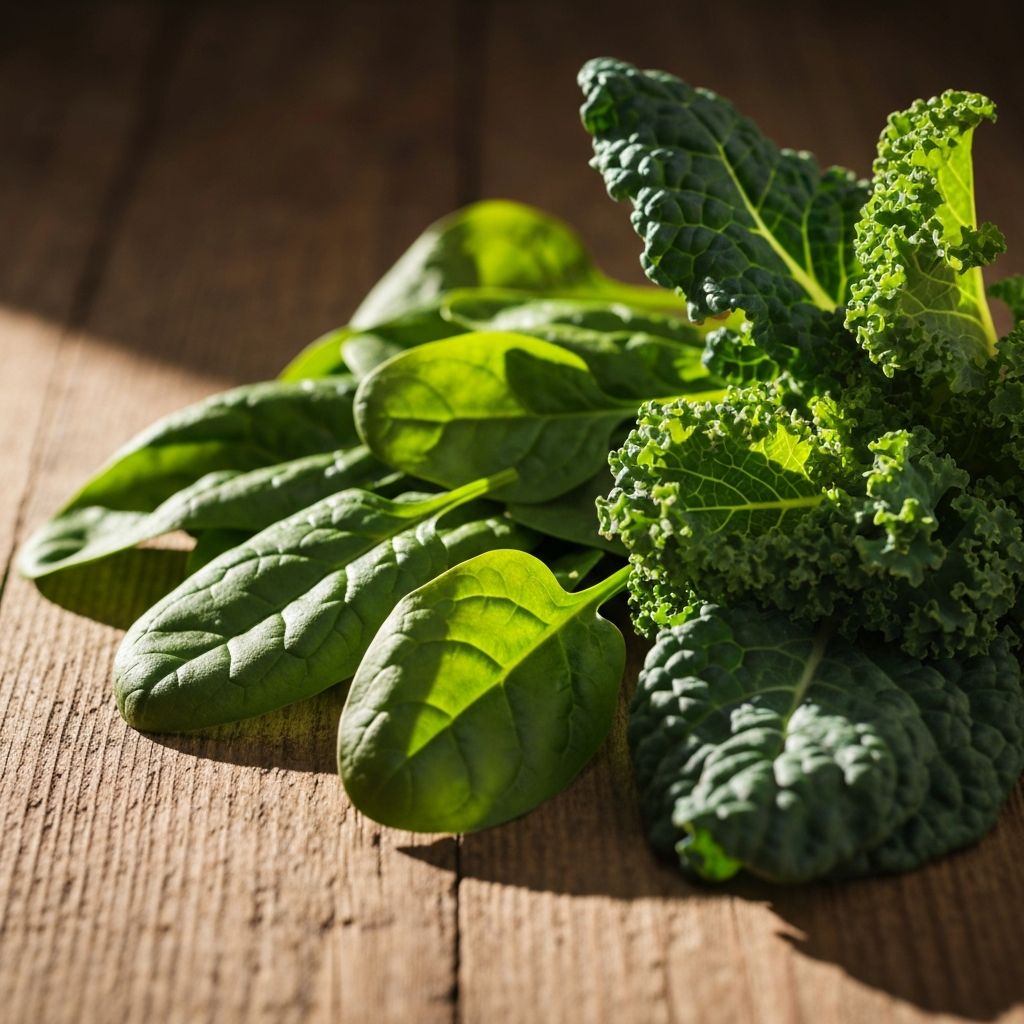

Leafy Greens
Leafy green vegetables such as spinach, kale, and lettuce are rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like iron and calcium. They are low in calories and high in fiber, making them a valuable addition to various meals.
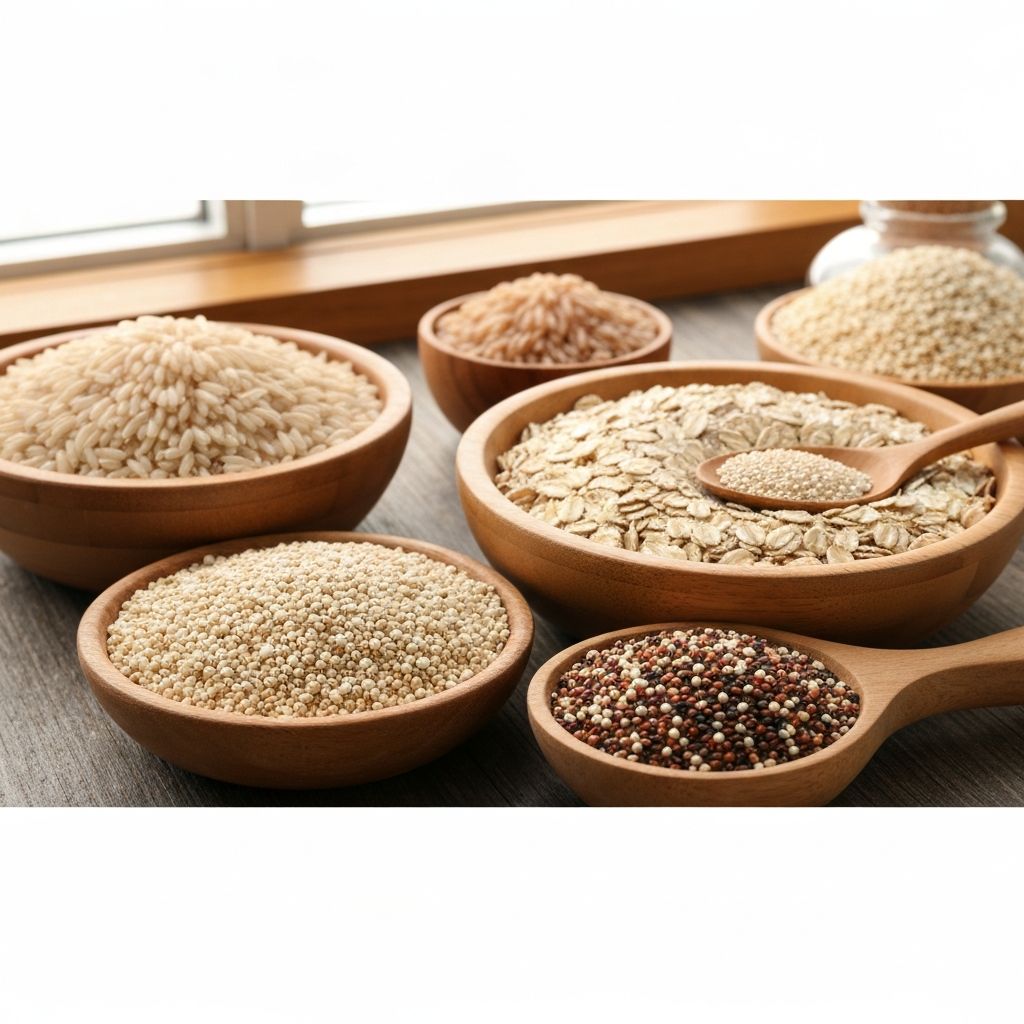

Whole Grains
Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and quinoa contain the entire grain kernel, providing fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. They offer sustained energy release and contribute to digestive health.
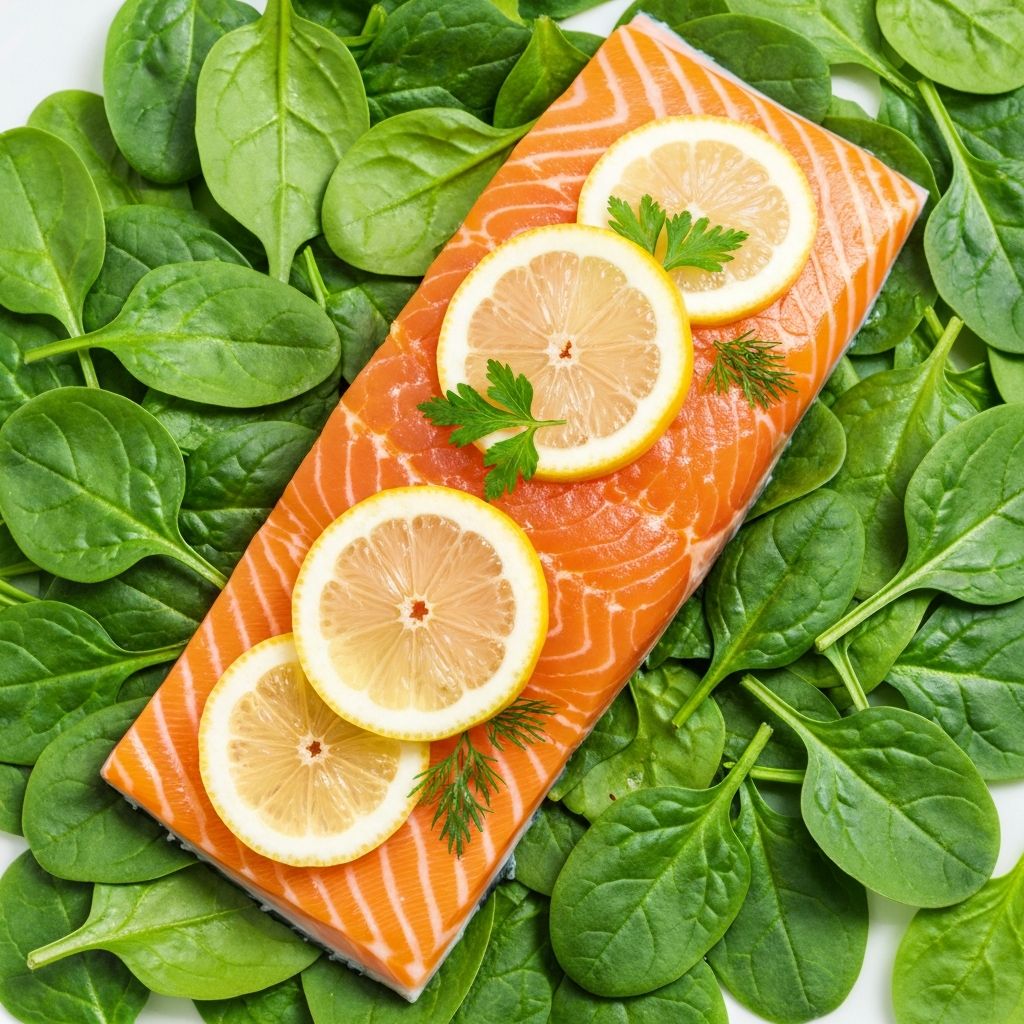

Lean Proteins
Lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, legumes, and tofu provide essential amino acids needed for tissue repair and maintenance. Fish varieties like salmon also contain omega-3 fatty acids.

Common Myths About Nutrition
There are numerous misconceptions about nutrition and diet that circulate in popular culture. Understanding what is factual and what is myth can help individuals make more informed decisions about their eating habits.
Some common myths include the belief that all fats are unhealthy, that carbohydrates should be completely avoided, or that skipping meals is an effective approach to weight management. Evidence-based nutrition science often contradicts these oversimplified claims.
Science-Backed Facts
Nutritional science is based on research and evidence from numerous studies. Here are some well-established facts about nutrition and diet:
- A varied diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides a wide range of essential nutrients.
- Fiber from plant-based foods supports digestive health and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and certain plant sources, play important roles in brain and heart health.
- Regular hydration is essential for all bodily functions and affects energy levels and cognitive performance.
- Nutrient needs can vary based on age, activity level, and individual health status.
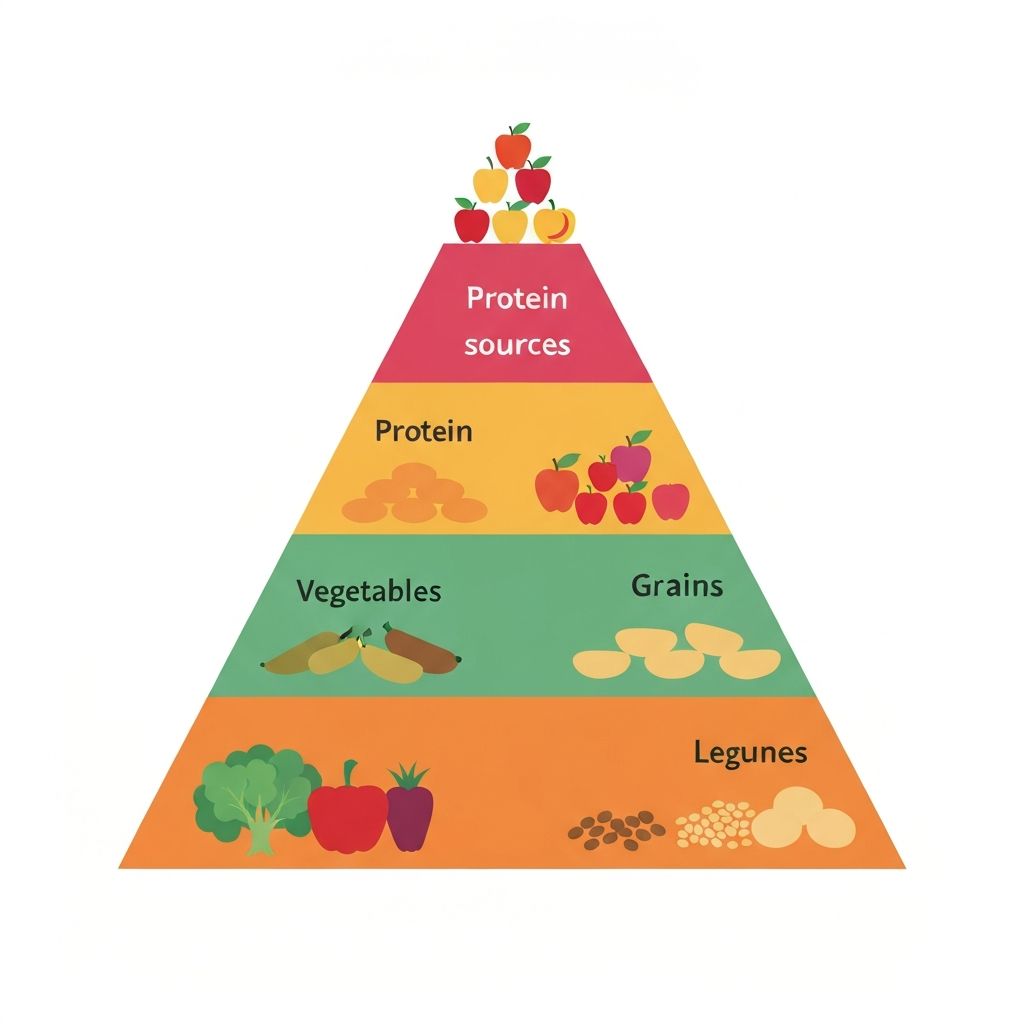
Visual Guide to Nutrition
Visual representations of nutritional concepts, such as food pyramids or plate models, can help illustrate the proportions of different food groups in a balanced diet. These tools serve as educational references for understanding dietary composition.
Such guides typically emphasize the importance of vegetables and fruits, followed by whole grains, then proteins, with smaller amounts of fats and oils. These visual aids are designed to simplify complex nutritional information.
Lifestyle Considerations
Nutrition is one component of overall lifestyle. Physical activity, sleep quality, stress management, and social connections all interact with dietary habits to influence health and wellbeing.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity complements a balanced diet. The type and intensity of physical activities can influence nutritional needs, particularly regarding energy and protein intake.
Individual Differences
Nutritional needs and optimal dietary patterns can vary significantly between individuals based on factors such as age, genetics, activity levels, and health status. What works well for one person may not be ideal for another.
Limitations and Context
The information provided on this website is educational in nature and describes general principles of nutrition. It is not intended as individual advice or recommendations. Dietary needs vary greatly among individuals, and there are many valid approaches to maintaining a balanced diet. This content does not replace consultation with qualified health or nutrition professionals who can provide personalized guidance based on individual circumstances.
Continue Learning
Understanding nutrition is an ongoing process. There is always more to learn about how different foods affect the body and how dietary patterns relate to health outcomes.
Learn More About Balanced Diet
Additional Resources
Expanding your knowledge about nutrition can involve exploring various educational materials, scientific publications, and reputable health information sources. Many organizations provide evidence-based information on dietary patterns and nutritional science.
Reading diverse sources and staying informed about current research can help develop a more comprehensive understanding of nutrition and its role in daily life.
Read More